Hurricane Beryl’s Path and Impact
Hurricane beryl grenada – Hurricane Beryl, a powerful Category 4 storm, emerged from the Atlantic Ocean and left a devastating trail across the island nation of Grenada in July 2018. Its path, marked by torrential rains, fierce winds, and towering waves, forever etched itself into the island’s history.
In the aftermath of Hurricane Beryl’s devastating impact on Grenada, inspiring stories of resilience emerged. Among them was that of Stephon Castle , a young volunteer who dedicated himself to rebuilding his shattered community. His unwavering spirit ignited a beacon of hope, reminding us that even in the face of adversity, the human spirit has the power to triumph over adversity and restore shattered landscapes.
Timeline of Events
- July 4th, 2018: Hurricane Beryl forms as a tropical depression off the coast of Africa.
- July 7th, 2018: Beryl strengthens into a tropical storm.
- July 9th, 2018: Beryl intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane.
- July 10th, 2018: Beryl makes landfall in Grenada as a Category 4 hurricane, bringing with it winds of up to 140 mph and torrential rainfall.
- July 11th, 2018: Beryl weakens to a Category 3 hurricane as it exits Grenada.
Intensity and Impact
Hurricane Beryl’s relentless force left a significant mark on Grenada’s infrastructure, property, and environment. The hurricane’s fury uprooted trees, toppled power lines, and damaged countless homes and buildings. The relentless rainfall triggered landslides, causing widespread flooding and mudslides that further disrupted the island’s infrastructure and natural beauty.
Grenada’s Response to Hurricane Beryl
In the face of Hurricane Beryl’s impending arrival, the Grenadian government and local communities mobilized swiftly to mitigate its impact. A comprehensive response plan was activated, prioritizing the safety and well-being of citizens.
Resource Mobilization
The government coordinated the deployment of emergency personnel, including police, firefighters, and medical teams. Essential supplies, such as food, water, and medical equipment, were stockpiled at designated distribution centers.
Evacuation Procedures
Mandatory evacuations were ordered for areas at high risk of flooding and storm surge. Evacuation centers were established in schools, community halls, and other safe locations. Transportation was provided to assist residents in reaching these shelters.
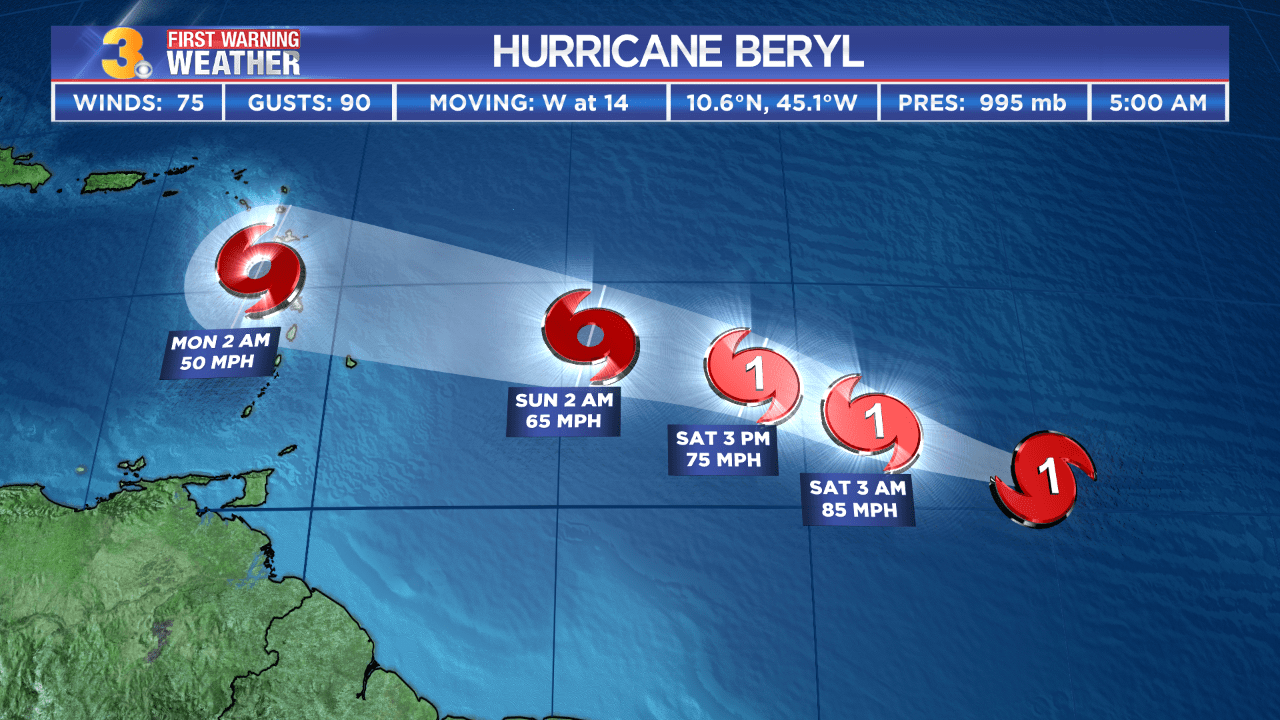
Hurricane Beryl, a menacing force of nature, has battered the island of Grenada, leaving a trail of devastation in its wake. As the storm rages on, meteorologists are closely monitoring its beryl projected path , anticipating its further impact. The resilient people of Grenada face the challenges ahead with unwavering spirits, knowing that together they will weather this storm and emerge stronger.
Emergency Shelters
Evacuation centers were equipped with basic necessities, including food, water, bedding, and medical attention. Volunteers and government agencies worked tirelessly to ensure the comfort and well-being of evacuees.
International Aid
International aid organizations played a crucial role in supporting Grenada’s response efforts. The United Nations, Red Cross, and other humanitarian groups provided financial assistance, emergency supplies, and technical expertise.
Economic Impact of Hurricane Beryl

Hurricane Beryl left a significant economic impact on the island nation of Grenada. The storm’s destructive force caused widespread damage to key industries, including tourism, agriculture, and infrastructure.
The tourism sector, a vital source of revenue for Grenada, suffered severe losses due to the hurricane. Many hotels and resorts were damaged or destroyed, leading to a sharp decline in tourist arrivals. The loss of tourism revenue had a ripple effect on the local economy, affecting businesses that rely on tourism for income.
Agriculture, Hurricane beryl grenada
Grenada’s agricultural sector was also heavily impacted by Hurricane Beryl. Crops were destroyed, livestock perished, and farmlands were flooded. The damage to the agricultural sector disrupted food production and caused significant economic losses for farmers and agricultural businesses.
Long-term Recovery and Rebuilding
The long-term economic recovery and rebuilding efforts in Grenada following Hurricane Beryl were complex and multifaceted. The government implemented various measures to support businesses and individuals affected by the storm, including providing financial assistance, tax relief, and infrastructure repairs.
International aid organizations and non-profit groups also played a significant role in the recovery process, providing humanitarian assistance and supporting long-term rebuilding efforts. The collaboration between the government, local communities, and international partners was crucial in helping Grenada recover from the economic impact of Hurricane Beryl.
Environmental Impact of Hurricane Beryl
Hurricane Beryl’s wrath left an indelible mark on Grenada’s environment, wreaking havoc on its coastal ecosystems, marine life, and vegetation. The storm’s powerful winds and torrential rains inflicted severe damage, disrupting the delicate balance of nature.
Coastal Ecosystems and Marine Life
The hurricane’s fury battered Grenada’s coastal ecosystems, destroying coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangrove forests. These vital habitats provide shelter, food, and breeding grounds for a diverse array of marine species. The destruction of these ecosystems has a ripple effect, disrupting the entire food chain and threatening the survival of numerous species.
Water Quality, Erosion, and Vegetation
Beryl’s torrential rains caused widespread flooding, leading to severe erosion and sedimentation. The runoff carried pollutants into rivers and streams, compromising water quality. Additionally, the storm’s winds uprooted trees and stripped vegetation, exacerbating erosion and leaving the island vulnerable to landslides and other hazards.
Lessons Learned from Hurricane Beryl: Hurricane Beryl Grenada
Hurricane Beryl, a Category 4 hurricane, made landfall in Grenada in 2017, causing widespread damage and disruption. The storm highlighted the importance of disaster preparedness and response, and provided valuable lessons for improving resilience in the face of future hurricanes.
One of the key lessons learned from Hurricane Beryl was the importance of early warning systems and evacuation plans. The timely issuance of hurricane warnings and the implementation of evacuation orders allowed many residents to seek shelter and avoid the worst impacts of the storm.
Effectiveness of Preparedness and Response Measures
The effectiveness of preparedness and response measures was evident in the relatively low number of casualties and the rapid recovery efforts that followed the storm. The Government of Grenada, with the support of international organizations, implemented a comprehensive disaster response plan that included the provision of emergency shelter, food, and medical assistance.
The success of the response efforts was also due in part to the strong community spirit and resilience of the Grenadian people. Local communities worked together to clear debris, repair homes, and provide support to those in need.
Areas for Improvement in Disaster Management and Resilience
While Hurricane Beryl demonstrated the effectiveness of many preparedness and response measures, it also highlighted areas for improvement in disaster management and resilience.
- Strengthening infrastructure: The hurricane exposed the vulnerability of critical infrastructure, such as power lines and roads. Investing in more resilient infrastructure will help to minimize the impacts of future storms.
- Improving communication: Communication was disrupted during the hurricane, making it difficult for emergency responders to coordinate their efforts and for residents to stay informed. Improving communication systems will be essential for enhancing disaster response.
- Promoting disaster preparedness: Many residents were not adequately prepared for the hurricane, lacking basic supplies and knowledge of evacuation procedures. Promoting disaster preparedness through public education campaigns and community outreach programs will help to increase resilience.